Emacs Introduction
Some common keyboard shortcut of emacs are listed below:
| Command | Shortcut |
|---|---|
| Open(“visit”) file | C-x C-f |
| Save current buffer(an open file) | C-x C-s |
| Save as [another name] | C-x C-w |
| Quit Emacs | C-x C-c |
| Suspend Emacs | C-z |
| Resume Emacs(when it is suspended) | fg |
| Undo | C-_ |
| Set mark(then you can select a region text using your cursor) | C-@ |
| Cut(Kill) | C-w |
| Copy | M-w |
| Paste | C-y |
| Page down(up) | C-v(M-v) |
Search word in Emacs:
| Command | Shortcut |
|---|---|
| Enter isearch mode | M-x isearch-forward (then you can enter the keyword) |
| Jump to next occurrence | C-s |
| Jump to previous occurrence | C-r |
| Exit and place the cursor at origin position | C-g |
| Exit and place the cursor at current position | Enter |
Valgrind Introduction
Valgrind is actually a collection of tools, which are designed so that more can be added if desired. In here, we more focused on the Memcheck tool, which allowed us to check whether our program has some memory leak(e.g. caused by malloc but no free, dangle pointer…)
How to use?
Simply run your program with valgrind command with the argument your program need valgrind ./myProgram hello 42
What to expect
if you run the command above, you should expect the following output, says:
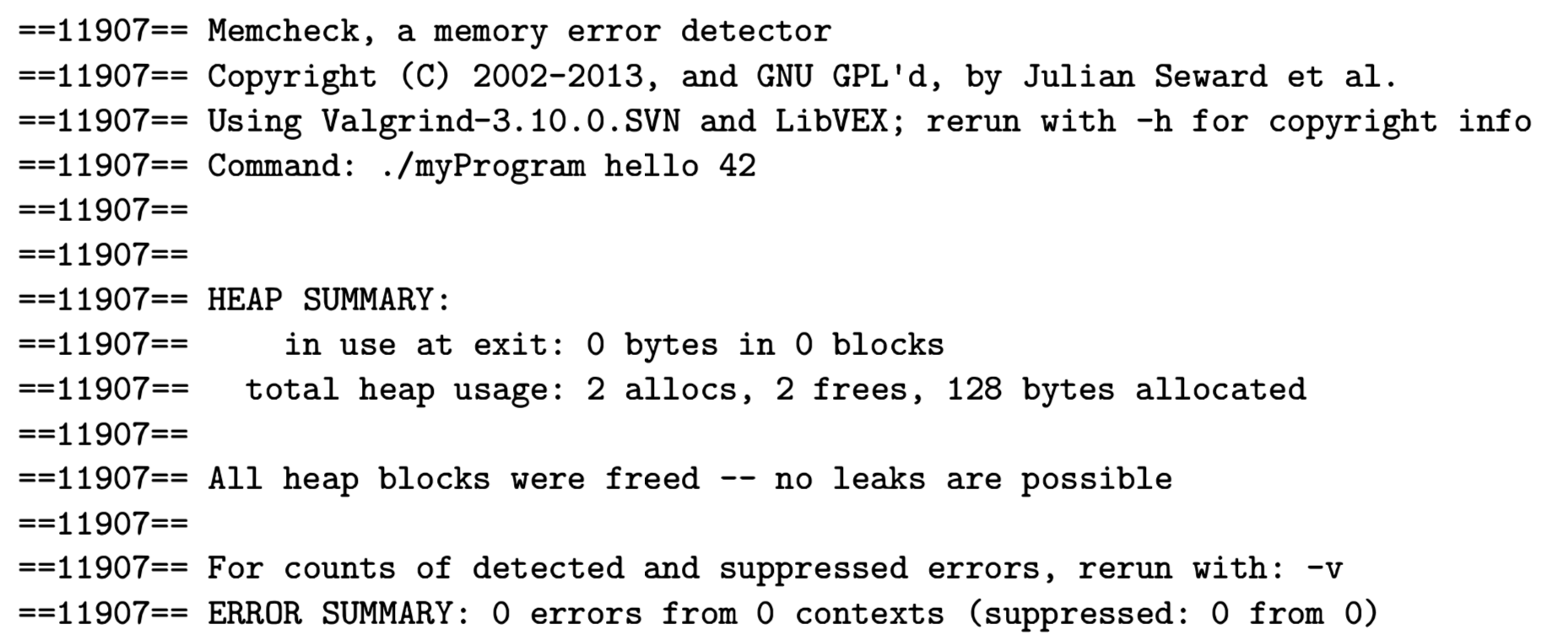
- All heap blocks were freed – no leaks are possible
- ERROR SUMMARY: 0 errors from 0 contexts
What’s the typical error?

- Sometimes you just use some uninitialised value(especially you are using malloc)(e.g.
char * str = malloc(cnt * sizeof(* str)), this will leave the pointer str you created uninitialised, instead you should usecalloc,char * str = calloc(cnt * sizeof(* str)))

- Sometimes you may access some memory you are not suppose to access, for example
char * str1 = "Hello World";
char * str2 = calloc(cnt * sizeof(* str2));
strcpy(str2, str1);
note that strcpy will add a \0 at the end of the string, so you should allocate len + 1 size of memory
Useful command
valgrind --track-origins=yes --leak-check=full ./myProgram
--track-origins=yestells the valgrind to track exactly where each error happen--leak-check=fulltells the valgrind to show exactly where each memory leak error happen
MakeFile Introduction
for C, we use gcc to compile
CFLAGS=-std=gnu99 -pedantic -Wall -Werror -ggdb3
all: main.o
gcc -o rand_story $(CFLAGS) main.o
main.o: main.c catarray.h
gcc -c $(CFLAGS) main.c
.PHONY: clean
clean:
rm -r rand_story *.o *~
for C++, we use g++ to compile
CFLAGS= -pedantic -Wall -Werror -ggdb3
all: code.o
g++ -o code_output $(CFLAGS) code.o
code.o: code.cpp
g++ -c $(CFLAGS) code.cpp
.PHONY: clean
clean:
rm -r code_output *.o *~
